Cervical fluid is an essential yet often overlooked indicator of menstrual and reproductive health. This fluid, produced by the cervix, changes consistency and quantity throughout the menstrual cycle due to hormonal fluctuations. By understanding cervical fluid before period and its changes, you can gain insight into fertility, hormonal balance, and menstrual health. This article explains the various aspects of cervical fluid, its stages, and how it connects to overall wellness.
What Is Cervical Fluid?
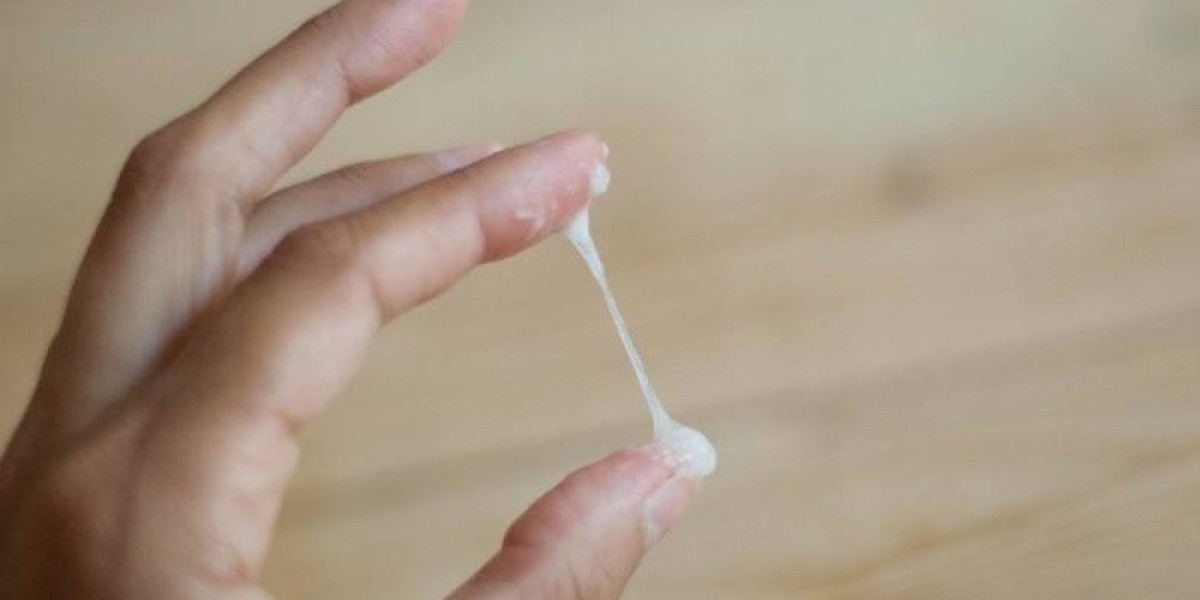
Cervical fluid, also known as cervical mucus, is a secretion from the cervix that plays an important role in reproductive health. It not only facilitates the movement of sperm but also helps maintain vaginal health by clearing out bacteria. Cervical mucus before menstruation varies in consistency, amount, and appearance during the menstrual cycle and is influenced by hormonal changes.
Why Does Cervical Fluid Change Throughout the Cycle?
Cervical fluid changes throughout the menstrual cycle due to hormonal shifts involving estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen levels rise in the first half of the cycle, resulting in increased, watery, and stretchy cervical fluid to help sperm move more easily. After ovulation, progesterone dominates, causing the fluid to become thicker and creating a barrier to sperm.
The Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
Follicular Phase:
During the follicular phase, cervical fluid is typically dry or minimal initially. As estrogen levels rise, the fluid becomes more noticeable and may appear creamy, then more watery and stretchy as ovulation approaches.
Ovulation Phase:
Cervical fluid is most fertile at ovulation. It often resembles raw egg whites—clear, stretchy, and abundant. This fluid type helps sperm travel through the cervix to meet the egg, making it the most fertile stage of the cycle.
Luteal Phase:
In the luteal phase, after ovulation, progesterone increases, causing the cervical fluid to thicken or become sticky. This change helps prevent additional sperm from entering the uterus as the body prepares for potential pregnancy or the next cycle.
Cervical Fluid Before Period
Characteristics of Cervical Fluid Right Before Period:
In the days leading up to a period, cervical fluid often becomes scant or dry. It may appear sticky or creamy if it is present, as progesterone levels have peaked and estrogen is low. This type of fluid typically signals that the fertile window has closed. Cervical Fluid Before Period is usually minimal or absent, reflecting the body's preparation for menstruation.
Why Cervical Fluid Changes Happen:
The cervical fluid's fluctuations serve functional purposes, from creating a friendly environment for sperm to protecting the uterus from bacteria. These changes correlate with the menstrual cycle phases and hormonal variations, offering insight into fertility and cycle timing.
Types of Cervical Fluid Before Period
Dry or Minimal Cervical Fluid:
Right before menstruation, many women experience little or no cervical fluid, often feeling dry. This phase is influenced by low levels of both estrogen and progesterone.
Creamy Cervical Fluid:
Creamy cervical fluid appears thick, white, or pale yellow and may feel lotion-like. It typically shows up before the period starts and signals that the body is less fertile.
Sticky or Thick Cervical Fluid:
Sticky cervical fluid is denser and appears pasty or clumpy. It usually signals the luteal phase. This type of fluid prevents sperm from entering the cervix, maintaining a closed state in preparation for menstruation.
What Cervical Fluid Can Tell You About Your Fertility and Health
Tracking Fertility Using Cervical Fluid:
Observing cervical fluid is one of the easiest and most natural methods to track fertility. Fertile cervical fluid (stretchy, clear, and abundant) indicates ovulation, while thicker or absent fluid suggests non-fertile days.
How Cervical Fluid Reflects Hormone Health:
Estrogen and progesterone influence cervical fluid changes, which affect fluid quality and quantity. Consistent irregularities in cervical fluid can suggest hormonal imbalances, potentially indicating underlying health concerns.
How Organic Sanitary Pads Support Menstrual Health
Benefits of Using Organic Pads for Sensitive Skin:
Organic sanitary pads are made without harmful chemicals, dyes, or synthetic materials, making them ideal for sensitive skin. They reduce the risk of irritation and allergic reactions, supporting the health of the sensitive vulvar area.
Reducing Chemical Exposure with Organic Pads:
Conventional sanitary pads often contain chemicals that can disrupt hormonal health and impact vaginal flora. Organic pads from natural materials minimize chemical exposure and provide a safer, healthier option.
Using Cervical Fluid Awareness to Choose Menstrual Products
How Your Cycle and Cervical Fluid Affect Product Choice:
Cervical fluid can help you decide on appropriate menstrual products. During heavier fluid days, panty liners or organic pads might be helpful, while unique products that are breathable and natural are beneficial throughout the cycle to support vaginal health.
Environmental Impact of Organic Products:
Organic pads, typically biodegradable and produced using sustainable farming practices, have a lower environmental impact than conventional pads. Choosing organic products contributes to environmental preservation while prioritizing personal health.
Understanding the Role of Cervical Fluid in Pregnancy
Early Pregnancy and Cervical Fluid:
Increased estrogen may make cervical fluid more abundant and creamy in early pregnancy. This change often signals pregnancy early, although other symptoms must accompany it for confirmation.
How Cervical Fluid Patterns Change if Pregnancy Occurs:
If pregnancy occurs, cervical fluid may remain creamy and thick rather than drying up before the expected period. Increased cervical fluid is common, helping protect the uterus from infection during early pregnancy.
Tracking Cervical Fluid Changes Over Time
The Benefits of Keeping a Cycle Diary:
Maintaining a record of cervical fluid changes aids in understanding your cycle patterns, making it easier to identify fertile windows or potential health concerns. It provides a personal history that can be valuable during medical consultations or for fertility tracking.
Apps and Tools for Tracking Cervical Fluid:
Numerous apps assist in tracking cervical fluid changes, providing reminders and visual patterns to simplify monitoring. Apps such as Clue, Flo, and Fertility Friend offer features for detailed cycle tracking.
Conclusion
Cervical fluid is a vital indicator of menstrual health, offering insights into fertility, hormonal balance, and cycle phases. Observing changes in cervical fluid, especially Cervical Fluid Before Period, empowers you to make informed decisions regarding reproductive health and product choices. By choosing organic sanitary products, you further protect your well-being and support the environment, reducing exposure to potentially harmful chemicals. Embracing tools like cycle diaries and apps for tracking cervical fluid can deepen your understanding of your body, enhancing your health awareness and helping you confidently navigate your cycle.