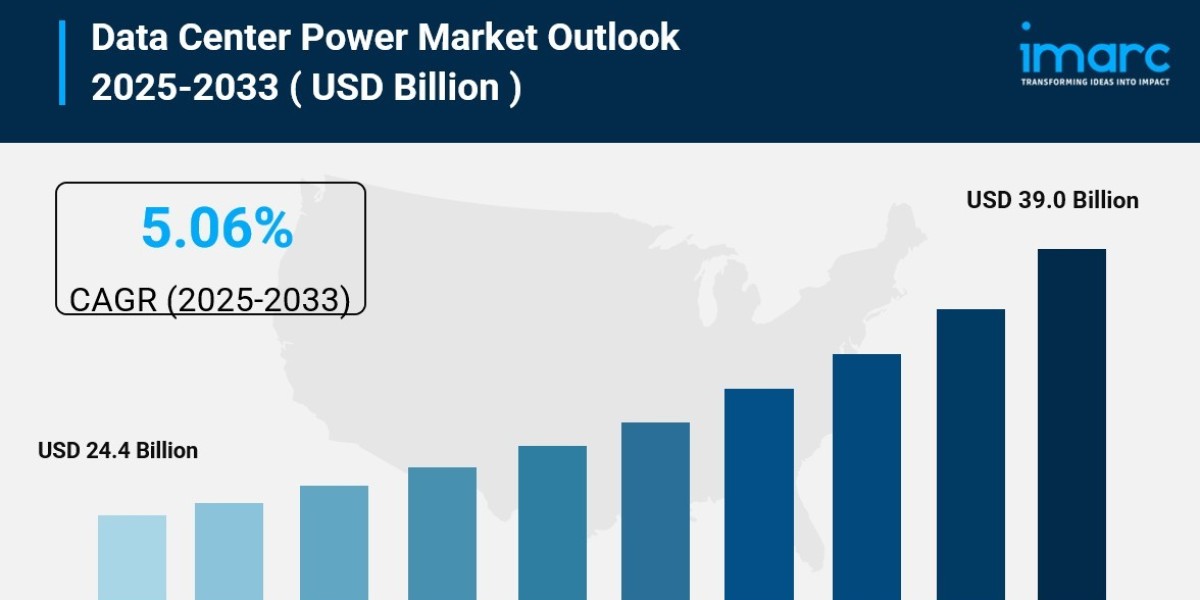
The global data center power market size reached USD 24.4 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 39.0 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.06% during 2025-2033. The market is experiencing steady growth driven by rapid digitization among enterprises, increasing adoption of cloud computing solutions, the growing need to store data on the cloud leading to establishment of mega data centers, and the rising preferences for advanced power distribution and management solutions due to inflating electricity prices.
Key Stats for Data Center Power Market:
- Data Center Power Market Value (2024): USD 24.4 Billion
- Data Center Power Market Value (2033): USD 39.0 Billion
- Data Center Power Market Forecast CAGR: 5.06%
- Leading Segment in Data Center Power Market in 2024: Power Distribution and Measurement
- Key Regions in Data Center Power Market: Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East and Africa
- Top companies in Data Center Power Market: ABB Ltd., Black Box (Essar Group), Cisco Systems Inc., CyberPower Systems, Delta Electronics Inc., Eaton Corporation plc, Fujitsu, Generac Power Systems Inc., General Electric, Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd., Legrand, Schneider Electric, Vertiv Co., etc.
Why is the Data Center Power Market Growing?
The data center power market is experiencing explosive growth as the digital transformation wave sweeps across every industry imaginable. Organizations worldwide are moving their operations to the cloud at an unprecedented pace, creating massive demand for data center infrastructure. This shift isn't just about storage anymore—it's about processing power for AI workloads, streaming services, online gaming, and the countless applications that make modern life possible.
What's really driving this surge is the sheer scale of data we're generating and consuming daily. A single ChatGPT query needs nearly 10 times as much electricity to process as a traditional Google search. That massive difference highlights why data centers are becoming one of the fastest-growing consumers of electricity globally. Goldman Sachs Research forecasts that global power demand from data centers will increase 50% by 2027 and potentially 165% by the end of the decade compared to baseline levels.
Electricity costs have skyrocketed in areas near data centers—wholesale electricity now costs as much as 267% more than five years ago in some US regions with heavy data center concentration. This dramatic rise is being passed on to customers and has made power management absolutely critical for data center operators. They're no longer just concerned about uptime—they're laser-focused on efficiency, sustainability, and cost optimization.
The numbers tell a compelling story. Between 2024 and 2030, electricity demand for data centers in the United States alone is expected to increase by approximately 400 terawatt-hours. BloombergNEF forecasts that US data center power demand will more than double by 2035, rising from almost 35 gigawatts in 2024 to 78 gigawatts. The actual energy consumption growth will be even steeper, with average hourly electricity demand nearly tripling during this period.
Organizations are responding by investing heavily in advanced power management solutions. Power Distribution Units (PDUs), Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems, generators, and sophisticated battery monitoring systems are no longer optional—they're mission-critical infrastructure. These technologies help distribute energy from utility grids to data center racks efficiently while maintaining lower Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) ratios, which directly translates to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
The shift toward sustainable energy sources is gaining serious momentum. According to an S&P Global report, the US data center sector alone had contracted 50 gigawatts of clean energy by the end of Q3 2024. Solar dominated supply with 29 gigawatts, followed by wind at 13 gigawatts. This aggressive procurement of renewable energy reflects both environmental commitments and practical business needs—data centers operate 24/7 and need reliable, cost-effective power sources.
Corporate investment in this space is staggering. Eight major hyperscalers expect a 44% year-over-year increase to USD 371 billion in 2025 specifically for AI data centers and computing resources. In capital expenditure terms, hyperscalers surpassed traditional capital-intensive utilities in 2024, a trend that's expected to continue. From August 2024 to January 2025 alone, total data center deal value reached USD 50 billion.
The modular data center segment is particularly interesting, growing from USD 32.6 Billion in 2024 and projected to hit USD 102.5 Billion by 2033. These prefabricated, scalable solutions offer faster deployment and greater flexibility compared to traditional builds. Mega data centers are also proliferating rapidly—this segment reached USD 26.8 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 40.6 Billion by 2033, driven by the insatiable demand for cloud services.
Geographic expansion is another key driver. Data center capacity in the Asia Pacific region is projected to double in the coming years as traditional computing demand combines with AI workloads. Emerging markets are investing heavily in digital infrastructure, recognizing that data centers are essential for economic competitiveness in the modern era.
The reliability equation has also changed dramatically. Modern businesses can't afford downtime—even minutes of outage can cost millions in lost revenue and damaged reputation. Advanced power backup systems ensure uninterrupted operation even during large-scale power outages, making these solutions indispensable for enterprises that operate globally around the clock.
Related Sample URL: https://www.imarcgroup.com/data-center-power-market/requestsample
AI Impact on the Data Center Power Market:
Artificial intelligence is fundamentally reshaping the data center power landscape, creating both unprecedented challenges and remarkable opportunities. The AI revolution isn't just increasing demand for electricity—it's transforming how data centers are designed, operated, and powered from the ground up.
The scale of AI's power requirements is staggering. Training large language models and running generative AI applications consume exponentially more energy than traditional computing workloads. A typical AI query can require 10 times the computational power of a standard search, translating directly to massive electricity consumption. This has created urgent pressure on data center operators to find innovative power solutions that can handle these intensive workloads without breaking the bank or the grid.
AI is simultaneously part of the problem and the solution. While AI workloads drive unprecedented power demand, AI-powered management systems are revolutionizing how data centers optimize energy consumption. Intelligent power management platforms use machine learning algorithms to predict load patterns, optimize cooling systems, and dynamically allocate resources based on real-time demand. These systems can reduce power consumption by 15-30% compared to traditional management approaches.
Advanced AI analytics are enabling predictive maintenance for power infrastructure. Instead of following fixed maintenance schedules, data centers can now use AI to monitor equipment health in real-time, predicting failures before they occur. This prevents costly downtime and extends equipment life, significantly reducing total cost of ownership. The technology analyzes thousands of data points from UPS systems, generators, PDUs, and cooling equipment to identify patterns that human operators might miss.
Digital twins powered by AI are becoming standard practice in data center planning and optimization. These virtual replicas allow operators to simulate different scenarios—from equipment failures to capacity expansions—before making physical changes. Operators can test various power configurations, cooling strategies, and load distributions virtually, identifying the most efficient approaches before investing in actual hardware.
The emergence of AI-specific data center designs is creating new markets for specialized power solutions. AI workloads generate more heat and require more consistent power delivery than traditional computing. This has sparked innovation in liquid cooling systems, high-density power distribution, and advanced battery technologies that can handle the unique demands of AI infrastructure.
Edge AI is pushing data processing closer to end users, creating demand for distributed power solutions that differ significantly from centralized data center designs. These edge locations need compact, efficient power systems that can operate reliably with minimal human intervention. AI-powered remote monitoring and management make this distributed model feasible at scale.
The race to power AI has sparked renewed interest in alternative energy sources. In 2024, Google struck a deal with Kairos Power to build out 500 megawatts of small nuclear reactors by the mid-2030s. Equinix partnered with small reactor developer Oklo—backed by OpenAI's Sam Altman—to build 20 micro reactors specifically for data center applications. These partnerships signal that the industry recognizes conventional power sources won't suffice for the AI-driven future.
AI is also accelerating the integration of renewable energy into data center operations. Intelligent systems can predict when solar and wind power will be available and automatically shift high-intensity workloads to take advantage of clean energy when it's abundant. This dynamic load management helps data centers reduce their carbon footprint while maintaining performance and reliability.
The financial implications are enormous. AI-driven power optimization systems can save data centers millions annually in electricity costs alone. More importantly, they enable facilities to maximize capacity utilization without massive infrastructure upgrades. Instead of building new capacity, operators can use AI to squeeze more performance from existing systems.
However, the AI boom is creating infrastructure challenges that won't be solved quickly. Data centers to account for 9% of electricity demand in the US by 2035—an increase of 5 percentage points from current levels. The pace of AI development is outstripping the ability of power grids and generation facilities to keep up, forcing data center operators to become increasingly creative and strategic about power sourcing and management.
Segmental Analysis:
Analysis by Solution Type:
- Power Distribution and Measurement (Intelligent PDUs, Non-Intelligent PDUs, Monitoring)
- Power Backup
- Cabling Infrastructure
Power distribution and measurement solutions dominate the market, representing the largest segment. This category includes intelligent and non-intelligent Power Distribution Units (PDUs) that are absolutely essential for distributing electrical power efficiently throughout data center facilities. These systems have evolved far beyond simple power strips—modern intelligent PDUs offer real-time monitoring, remote management, and granular control over individual outlets.
The sophistication of monitoring capabilities has become a key differentiator. Advanced PDUs track power consumption at the rack level, outlet level, and even individual device level, providing operators with unprecedented visibility into energy usage patterns. This detailed data enables precise capacity planning and helps identify inefficiencies that would otherwise go unnoticed. The ability to remotely control power to specific devices has become critical for managing distributed infrastructure and troubleshooting issues without dispatching technicians.
Power backup solutions including UPS systems, generators, and battery storage represent another critical segment. These systems have become more sophisticated as downtime costs have skyrocketed and reliability requirements have intensified. Modern UPS systems don't just provide emergency power—they actively condition power quality, protecting sensitive equipment from voltage fluctuations and electrical noise that can cause data corruption or hardware failure.
The rise of lithium-ion battery technology has transformed the backup power landscape. While traditional lead-acid batteries still dominate in many installations, lithium-ion systems offer superior energy density, longer lifespans, and faster charging capabilities. They're particularly valuable for high-density AI workloads where space is at a premium and power demands are unpredictable.
Cabling infrastructure, while sometimes overlooked, plays a vital role in data center power management. High-quality power cables, structured wiring systems, and proper cable management are essential for maintaining efficiency and safety. Poor cabling can create resistance that wastes energy as heat, reduces system reliability, and makes maintenance nightmarishly complex. Modern data centers invest heavily in organized, well-documented cabling systems that support scalability and simplify upgrades.
Analysis by Service Type:
- System Integration
- Training and Consulting
- Support and Maintenance
System integration services are experiencing robust demand as data centers become increasingly complex. Organizations need expert help designing, implementing, and optimizing power infrastructure that integrates seamlessly with cooling systems, IT equipment, and building management platforms. Integration specialists ensure that all components work together efficiently, minimizing waste and maximizing reliability.
The complexity of modern data center power systems means that few organizations have all the expertise in-house. Integration services bridge this gap, bringing together power distribution, backup systems, monitoring platforms, and control software into cohesive solutions. These specialists understand the interdependencies between different systems and can design architectures that avoid single points of failure while maintaining operational efficiency.
Training and consulting services are growing rapidly as the knowledge gap widens between available technology and operator capabilities. Data center staff need training on new power management platforms, AI-driven optimization tools, and emerging technologies like liquid cooling and edge power distribution. Consulting services help organizations develop long-term power strategies that align with business growth projections and sustainability goals.
Industry-specific training has become essential. Power management for AI workloads differs significantly from traditional computing, and operators need specialized knowledge to handle these unique requirements safely and efficiently. Consulting firms are helping data centers navigate the transition to renewable energy, design hybrid power systems, and implement best practices for efficiency optimization.
Support and maintenance services represent the largest ongoing expense for most data center operators. These services ensure power infrastructure remains operational, performs optimally, and stays current with technology evolution. Preventive maintenance programs catch problems before they cause outages, while 24/7 support services provide rapid response when issues arise unexpectedly.
The shift toward predictive maintenance powered by AI analytics is transforming how support services are delivered. Instead of routine inspections on fixed schedules, maintenance teams can focus resources on equipment that analytics identify as at-risk. This targeted approach reduces costs while actually improving reliability by catching subtle degradation patterns that human inspectors might miss.
Analysis by Size:
- Mid-Size Data Center
- Enterprise Data Center
- Large Data Center
Large data centers dominate market share, reflecting the economies of scale that make hyperscale facilities attractive for cloud providers and major enterprises. These massive facilities, often consuming 10 megawatts or more of power, can negotiate better electricity rates, invest in cutting-edge efficiency technologies, and spread overhead costs across thousands of racks. The largest facilities now consume as much electricity as small cities, making power management absolutely critical to their operations.
Enterprise data centers represent a substantial market segment serving organizations that need dedicated infrastructure for sensitive workloads, regulatory compliance, or performance-critical applications. While smaller than hyperscale facilities, these data centers face similar challenges around efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. Many are upgrading aging infrastructure to handle modern workloads and improve power efficiency ratios.
Mid-size data centers fill an important niche, offering capabilities beyond what edge facilities can provide while maintaining more flexibility than massive hyperscale installations. These facilities often serve regional markets, support specialized industries, or provide disaster recovery capabilities for larger enterprises. Their power requirements typically range from 1-10 megawatts, making them significant consumers while remaining manageable from an infrastructure perspective.
Analysis by Vertical:
- BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance)
- Telecommunication and IT
- Energy
- Manufacturing
- Others
The BFSI sector represents one of the largest consumers of data center power, driven by stringent regulatory requirements, massive transaction volumes, and the need for always-on availability. Financial institutions cannot tolerate downtime—even seconds of outage during trading hours can cost millions and damage reputations irreparably. This makes redundant power systems, sophisticated backup capabilities, and meticulous power quality management essential investments.
Banking and financial services are also at the forefront of AI adoption for fraud detection, algorithmic trading, risk analysis, and customer service. These AI workloads are pushing power consumption higher while simultaneously demanding more sophisticated power management to maintain the 99.999% uptime that financial operations require.
Telecommunication and IT companies are obviously huge consumers of data center power as they provide the infrastructure that connects our digital world. These organizations operate some of the largest data centers globally, housing everything from content delivery networks to cloud computing platforms. The 5G rollout has intensified power demands as network densification requires more edge computing facilities with robust power infrastructure.
The energy sector itself has become a significant data center user as it digitizes operations, implements smart grid technologies, and uses AI for exploration, production optimization, and renewable energy forecasting. The irony of the energy industry consuming massive amounts of data center power isn't lost on industry observers, but it reflects how essential data analytics has become for modern energy operations.
Manufacturing is rapidly increasing its data center footprint as Industry 4.0 initiatives digitize production lines, implement IoT sensors, and use AI for quality control and predictive maintenance. Modern factories generate tremendous data volumes that require real-time processing, driving demand for on-site or nearby data centers with reliable power infrastructure.
Analysis of Data Center Power Market by Regions:
- Asia Pacific
- Europe
- North America
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
North America leads the global market, driven by the concentration of major technology companies, hyperscale data center operators, and early adoption of cloud services. The United States alone houses a substantial portion of global data center capacity, with major hubs in Virginia, California, Texas, and other states investing heavily in power infrastructure to support continued growth.
The region's well-developed electrical grid infrastructure and access to diverse power sources give it competitive advantages, though grid capacity is becoming strained in some high-density areas. Innovative power procurement strategies are emerging—Google's announcement of a USD 25 billion investment in data center and AI infrastructure over two years across states in the largest US electric grid demonstrates the scale of ongoing expansion. The company is also investing USD 3 billion to modernize two hydropower plants, showing how data center operators are directly investing in power generation to secure reliable supply.
US data center power demand is projected to grow from almost 35 gigawatts in 2024 to 78 gigawatts by 2035, according to BloombergNEF. This doubling of capacity in just over a decade highlights the urgent need for power infrastructure investment and explains why utility stocks saw massive gains in 2024. GE Vernova, General Electric's energy spinoff, saw its stock rise 150% after going public in April 2024, driven largely by strong demand for gas turbines to address growing data center energy needs.
Europe represents a significant market characterized by stringent energy efficiency regulations and ambitious sustainability targets. European data centers face pressure to minimize carbon footprints while maintaining reliability and performance. This has driven innovation in renewable energy integration, advanced cooling technologies, and power optimization strategies that often exceed what's required in other regions.
European governments are actively supporting data center development while pushing for environmental responsibility. The combination of regulatory requirements and market demand is creating opportunities for companies offering sustainable power solutions, energy storage technologies, and efficiency optimization services.
Asia Pacific is experiencing explosive growth driven by rapid digitization, expanding middle classes, and massive investments in digital infrastructure. Data center capacity in the region is projected to double as governments recognize digital infrastructure as essential for economic competitiveness. Countries like China, India, Singapore, Japan, and Australia are all making substantial investments in data center power infrastructure.
The region faces unique challenges including diverse regulatory environments, varying electrical grid reliability, and different climate conditions that affect cooling and power requirements. However, these challenges are driving innovation in adaptive power solutions, hybrid power systems combining grid and on-site generation, and efficiency technologies suited for tropical climates.
Latin America and the Middle East/Africa regions are emerging markets with significant growth potential. These areas are investing in digital infrastructure to support economic development, attract foreign investment, and participate in the global digital economy. While current market share is smaller, growth rates are often higher as these regions build modern data center capabilities from the ground up.
What are the Drivers, Restraints, and Key Trends of the Data Center Power Market?
Market Drivers:
The data center power market is propelled by the explosive growth of cloud computing, which has fundamentally changed how organizations approach IT infrastructure. Instead of maintaining on-premises servers, businesses are migrating workloads to the cloud, concentrating computing power in massive data centers that require sophisticated power management. This consolidation creates economies of scale but also concentrates power demand in ways that require innovative solutions.
The AI revolution is driving unprecedented power requirements. Training large language models can consume as much electricity as hundreds of homes use in a year, and inference workloads add continuous power demand that never drops. The race to develop and deploy AI applications is pushing data center operators to secure more power capacity faster than ever before, creating urgent demand for power infrastructure expansion and optimization.
Rising electricity costs are forcing data center operators to prioritize efficiency. When electricity represents 30-40% of operational expenses, even modest improvements in Power Usage Effectiveness directly impact profitability. This economic pressure is driving adoption of advanced power management systems, renewable energy procurement, and infrastructure modernization that reduces waste.
Sustainability commitments from major corporations are reshaping power sourcing strategies. Companies have made public pledges to achieve carbon neutrality or 100% renewable energy, creating massive demand for clean power solutions. This isn't just public relations—investors, customers, and regulators are holding companies accountable for environmental performance, making sustainable power sourcing a business imperative.
The proliferation of edge computing is creating distributed power requirements that differ from traditional centralized data centers. Edge locations need compact, efficient, reliable power systems that can operate with minimal oversight. This is driving innovation in modular power solutions, remote monitoring technologies, and intelligent management platforms that can handle geographically distributed infrastructure.
5G deployment is accelerating edge computing adoption and creating new power infrastructure requirements. The low-latency promises of 5G require computing resources close to end users, multiplying the number of facilities that need reliable power infrastructure. This distributed model creates opportunities for companies offering scalable, standardized power solutions.
Government initiatives supporting digital infrastructure development are providing favorable conditions for data center investment in many regions. Tax incentives, streamlined permitting processes, and infrastructure investments in electrical grids are making it easier to build and operate data centers, directly benefiting the power management sector.
Market Restraints:
The data center power market faces significant challenges around grid capacity constraints. In many regions, existing electrical infrastructure cannot support the massive power demands of new data centers. Grid connection times are stretching from months to years in some high-demand areas, forcing operators to delay projects or consider alternative locations. This bottleneck is limiting market growth despite strong underlying demand.
Regulatory uncertainty around energy consumption and environmental impact creates hesitation among some investors and operators. Some jurisdictions are considering restrictions on new data center development or imposing carbon taxes that could significantly impact economics. Navigating varying regulations across different markets adds complexity and risk to expansion plans.
The high capital costs of power infrastructure represent a barrier, particularly for smaller operators. Redundant power systems, advanced UPS installations, backup generators, and sophisticated monitoring platforms require substantial upfront investment. While these systems pay off through improved reliability and efficiency, the initial capital requirements can be prohibitive for organizations with limited resources.
Supply chain challenges for critical power equipment have emerged as a constraint. Global demand for transformers, switchgear, UPS systems, and generators has surged faster than manufacturing capacity can scale. Lead times for some equipment have extended significantly, delaying projects and forcing operators to plan further ahead or accept alternative solutions.
Technical workforce shortages are limiting how quickly organizations can deploy and operate advanced power management systems. The specialized knowledge required to design, install, maintain, and optimize modern data center power infrastructure is in short supply. This skills gap is driving up labor costs and constraining the pace of innovation adoption.
Concerns about environmental impact are creating social and political resistance to data center development in some communities. Local opposition to power infrastructure projects, water usage for cooling, and aesthetic concerns can delay or block developments. This "not in my backyard" dynamic is forcing operators to invest more in community relations and environmental mitigation.
Market Key Trends:
AI-driven power management is revolutionizing data center operations, moving from reactive to predictive approaches. Intelligent systems analyze patterns across thousands of data points to optimize power distribution, predict equipment failures, and dynamically adjust to changing workloads. This technology is becoming standard practice rather than a competitive differentiator.
The shift toward renewable energy is accelerating dramatically. Data center operators contracted 50 gigawatts of clean energy in the US alone by Q3 2024, with solar dominating at 29 gigawatts. This isn't just about sustainability—renewable energy often offers cost advantages and price stability compared to fossil fuel alternatives. Long-term power purchase agreements with wind and solar farms are becoming standard practice for major operators.
Nuclear power is experiencing renewed interest as a solution for data center power needs. Small modular reactors and micro reactors offer the promise of reliable, carbon-free power specifically designed for industrial applications. Google's partnership with Kairos Power and Equinix's deal with Oklo signal that nuclear is being seriously considered as part of the data center power mix.
Liquid cooling technologies are gaining traction as power densities increase with AI workloads. Traditional air cooling struggles to handle the heat generated by high-performance computing clusters, making liquid cooling essential for next-generation facilities. This shift impacts power infrastructure design as liquid cooling systems have different electrical requirements than air-based approaches.
Modular and prefabricated power solutions are becoming more popular, offering faster deployment and greater flexibility than traditional build-outs. These standardized systems arrive ready to install, reducing construction timelines from months to weeks. The approach also improves quality control and makes capacity expansion more predictable.
Battery storage integration is transforming how data centers interact with electrical grids. Advanced battery systems don't just provide backup power—they enable load shifting, grid services, and renewable energy storage that improve overall system economics and resilience. Some data centers are generating revenue by providing grid stabilization services during peak demand periods.
Edge computing architectures are driving demand for distributed power solutions that differ significantly from centralized data center designs. These smaller, geographically dispersed facilities need compact, efficient power systems that can operate reliably with minimal human intervention. Standardized, remotely managed power platforms are emerging to address this need.
Digital twins for power infrastructure are becoming standard practice in planning and optimization. These virtual replicas allow operators to simulate scenarios, test changes, and optimize configurations without risking actual operations. The technology is particularly valuable for capacity planning and troubleshooting complex issues.
Ask An Analyst: https://www.imarcgroup.com/request?type=report&id=1653&flag=C
Leading Players of Data Center Power Market:
According to IMARC Group's latest analysis, prominent companies shaping the global data center power landscape include:
- ABB Ltd.
- Black Box (Essar Group)
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- CyberPower Systems
- Delta Electronics Inc.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Fujitsu
- Generac Power Systems Inc.
- General Electric
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- Legrand
- Schneider Electric
- Vertiv Co.
These industry leaders are at the forefront of innovation, developing next-generation power management solutions that address the unique challenges of modern data centers. They're investing heavily in research and development to create systems that deliver higher efficiency, greater reliability, and better integration with renewable energy sources and intelligent management platforms.
Strategic partnerships define much of the competitive landscape. Leading providers are collaborating with cloud service providers, data center operators, and renewable energy companies to develop integrated solutions that address multiple aspects of power management simultaneously. These partnerships accelerate innovation and help ensure that new technologies meet real-world operational requirements.
The focus on sustainability has become central to corporate strategies. These companies recognize that customers increasingly demand power solutions that minimize environmental impact while maintaining performance. This is driving development of more efficient components, better integration with renewable energy sources, and transparent reporting tools that help operators track and reduce their carbon footprints.
Global expansion remains a priority as data center development accelerates worldwide. Leading players are establishing manufacturing facilities, service centers, and partnerships in emerging markets to capture growth opportunities and provide local support. This geographic diversification also helps mitigate supply chain risks that have become more apparent in recent years.
Digital transformation of their own operations is enabling these companies to offer smarter, more connected products. IoT-enabled power distribution units, cloud-based monitoring platforms, and AI-powered analytics tools are becoming standard offerings that differentiate leaders from followers. The integration of operational technology with information technology is creating new value propositions.
The emphasis on comprehensive lifecycle services distinguishes market leaders. Beyond selling hardware, these companies offer design consultation, system integration, training programs, predictive maintenance services, and continuous optimization support. This service-oriented approach creates long-term customer relationships and recurring revenue streams.
Key Developments in Data Center Power Market:
The data center power market has witnessed transformative developments throughout 2024 and into 2025, reflecting both the challenges and opportunities created by explosive growth in AI and cloud computing. Here are the major developments reshaping the industry landscape:
In July 2025, Google announced a massive USD 25 billion investment in data center and artificial intelligence infrastructure over the following two years across states in the largest US electric grid. The investment specifically targets the PJM Interconnection, which serves 65 million people across 13 states. Additionally, Google committed USD 3 billion to modernize two hydropower plants, demonstrating how tech giants are taking direct responsibility for power generation infrastructure rather than simply consuming grid power.
The renewable energy procurement surge reached historic levels. By the end of Q3 2024, an S&P Global report revealed that the US data center sector alone had contracted 50 gigawatts of clean energy. Solar dominated with 29 gigawatts, followed by wind at 13 gigawatts. This aggressive procurement reflects both corporate sustainability commitments and practical recognition that renewable energy offers long-term cost stability compared to fossil fuel alternatives.
Nuclear power partnerships marked a significant strategic shift. Google struck a groundbreaking deal with Kairos Power in 2024 to build out 500 megawatts of small nuclear reactors by the mid-2030s. This represented the first major tech company commitment to dedicated nuclear capacity for data centers. Equinix followed with a partnership with Oklo—a company backed by OpenAI's Sam Altman—to build 20 micro reactors specifically for data center applications. These deals signal growing acceptance that nuclear power may be essential for meeting AI's insatiable energy demands.
GE Vernova's dramatic market performance highlighted the financial opportunity in data center power. After General Electric spun off its energy division in April 2024, GE Vernova's stock surged 150% driven primarily by demand for gas turbines to support data center energy needs. This demonstrated how data center power requirements are creating value across the entire energy supply chain, not just for direct power management vendors.
The data center deal market reached unprecedented scale. From August 2024 to January 2025, total data center deal value hit USD 50 billion. This figure encompasses construction, acquisitions, power purchase agreements, and infrastructure investments, reflecting the massive capital flows into data center development and the power systems that support them.
Eight major hyperscale providers announced plans for a 44% year-over-year increase to USD 371 billion in 2025 spending specifically for AI data centers and computing resources. This investment wave is driving demand for power infrastructure, creating opportunities for companies offering scalable, efficient solutions that can be deployed rapidly to support aggressive expansion timelines.
Lancium's innovative approach to power management gained attention with its 1,000-acre campus in Abilene expected to open in Q1 2025 with 250 megawatts of power, ramping up to 1.2 gigawatts in 2026. The minimum power requirement for Lancium's customers demonstrates how AI workloads are pushing data centers toward unprecedented power densities that require fundamentally different infrastructure approaches.
DeepSeek's February 2025 announcement of its V3 model achieving substantial improvements in power consumption showed that AI efficiency breakthroughs could moderate future power demand growth. This development suggested that while AI is driving power consumption higher, concurrent efficiency improvements may prevent the most extreme growth scenarios from materializing.
Utility sector transformation accelerated as data center demand reshaped power markets. Utility stocks experienced massive gains in 2024, outperforming broader market indices as investors recognized that data centers represent a fundamental shift in electricity demand patterns. This financial performance is attracting capital to grid infrastructure modernization and power generation capacity that will support continued data center growth.
The International Energy Agency launched a new Observatory on Energy, AI and Data Centres to gather comprehensive data on AI's electricity needs and track AI applications across the energy sector. This initiative reflects growing recognition at the highest policy levels that data center power consumption requires coordinated monitoring and strategic planning to ensure grid stability and environmental sustainability.
About Us:
IMARC Group is a global management consulting firm that helps the world's most ambitious changemakers to create a lasting impact. The company provides a comprehensive suite of market entry and expansion services.
IMARC offerings include thorough market assessment, feasibility studies, company incorporation assistance, factory setup support, regulatory approvals and licensing navigation, branding, marketing and sales strategies, competitive landscape and benchmarking analyses, pricing and cost research, and procurement research.
Contact US:
IMARC Group
134 N 4th St. Brooklyn, NY 11249, USA
Email: sales@imarcgroup.com
Tel No:(D) +91 120 433 0800
United States: +1-631-791-1145