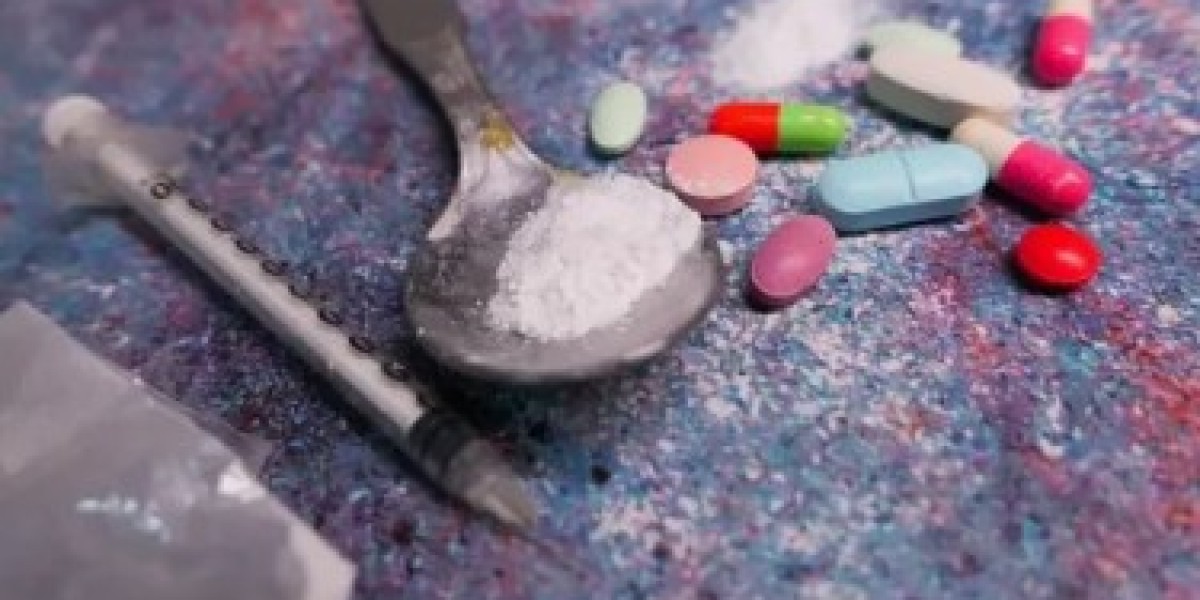
Substance abuse is a pervasive issue affecting millions of individuals and families worldwide. Whether it involves alcohol, prescription medications, or illicit drugs, addiction can have devastating effects on physical health, mental well-being, relationships, and overall quality of life. Thankfully, substance abuse treatment offers hope, guidance, and structured approaches to help individuals regain control and lead fulfilling lives.
What is Substance Abuse Treatment?
Substance abuse treatment refers to a range of therapeutic interventions designed to help individuals stop using drugs or alcohol, address underlying psychological issues, and prevent relapse. Effective treatment focuses not only on cessation but also on long-term recovery and personal development.
Treatment is highly individualized, as addiction manifests differently in every person. Factors such as the type of substance used, duration of addiction, co-occurring mental health disorders, and personal circumstances all influence the treatment plan.
Types of Substance Abuse Treatment
There are several approaches to substance abuse treatment, each suited to different levels of dependency and individual needs. Common treatment modalities include:
- Detoxification (Detox):
Detox is often the first step in the recovery process. It involves medically supervised withdrawal to help the body safely eliminate addictive substances. Detox addresses the physical symptoms of withdrawal and reduces the risk of severe complications, providing a foundation for further therapy. - Inpatient Rehabilitation Programs:
Inpatient or residential rehab programs provide 24-hour care in a structured environment. These programs are particularly beneficial for individuals with severe addiction or those who need to remove themselves from environments that trigger substance use. Patients receive medical supervision, counseling, and skill-building activities to support recovery. - Outpatient Treatment Programs:
Outpatient treatment allows individuals to live at home while attending therapy sessions regularly. This approach offers flexibility and is suitable for those with milder addictions or strong support systems. Outpatient programs often include individual counseling, group therapy, and educational sessions about coping strategies. - Behavioral Therapies:
Behavioral therapies are essential components of substance abuse treatment. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), contingency management, and motivational interviewing help patients recognize patterns of substance use, develop coping mechanisms, and stay motivated for long-term recovery. - Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT):
For certain addictions, especially opioids and alcohol, medications can significantly enhance recovery. MAT combines prescription medications with counseling and behavioral therapy to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Common medications include methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone. - Support Groups and Peer Counseling:
Support groups, such as 12-step programs, provide a community of individuals who share similar experiences. Peer support encourages accountability, reduces feelings of isolation, and fosters long-term commitment to recovery.
The Importance of Individualized Treatment Plans
No single treatment approach works for everyone. Substance abuse treatment must be tailored to meet the unique needs of each individual. Comprehensive assessments evaluate physical health, mental health, social environment, and addiction history to develop a customized treatment plan. Personalized treatment increases the likelihood of sustained recovery and addresses underlying issues such as trauma, anxiety, or depression that may contribute to substance use.
The Role of Mental Health in Substance Abuse Treatment
Mental health and substance use disorders often co-occur. Conditions like depression, anxiety, PTSD, or bipolar disorder can exacerbate addiction and make recovery more challenging. Integrated treatment that addresses both mental health and substance use is critical. This dual-diagnosis approach ensures that individuals receive the support they need to achieve holistic wellness.
Steps to Take Before Entering Treatment
Entering substance abuse treatment can feel overwhelming, but preparation can make the process smoother. Key steps include:
- Acknowledging the Problem:
Acceptance is the first step toward recovery. Recognizing that substance use has become a problem is essential for committing to treatment. - Seeking Professional Assessment:
A licensed addiction specialist or medical professional can evaluate the severity of addiction and recommend appropriate treatment options. - Choosing the Right Program:
Factors such as program type, duration, treatment methods, and insurance coverage should be considered. Visiting facilities, asking questions, and reviewing success rates can help individuals make informed decisions. - Preparing Support Systems:
Recovery is easier with a strong network of family, friends, or support groups. Communicating the decision to seek treatment and enlisting support helps maintain motivation.
Overcoming Challenges During Treatment
Recovery from addiction is rarely linear. Individuals may face physical discomfort, emotional struggles, and social pressures during treatment. Common challenges include:
- Withdrawal Symptoms: These can range from mild to severe, depending on the substance and level of dependence.
- Cravings and Triggers: Situations, people, or places associated with substance use can trigger cravings. Treatment programs teach coping strategies to manage these triggers.
- Emotional and Mental Health Struggles: Anxiety, depression, or past trauma may resurface during recovery. Ongoing counseling and therapy are crucial for navigating these challenges.
Despite these obstacles, persistence, structured support, and professional guidance significantly increase the likelihood of successful recovery.
Long-Term Recovery and Relapse Prevention
Substance abuse treatment is not just about stopping substance use—it’s about building a sustainable, healthy lifestyle. Long-term recovery strategies include:
- Aftercare Programs: Outpatient therapy, support groups, and sober living environments help maintain structure and accountability post-treatment.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Exercise, balanced nutrition, hobbies, and mindfulness practices promote physical and mental wellness.
- Skill Development: Learning stress management, communication skills, and coping strategies reduces the risk of relapse.
- Ongoing Support: Maintaining connections with supportive peers and mentors helps individuals navigate challenges without returning to substance use.
Relapse is a common part of recovery, but it does not signify failure. Early recognition and prompt intervention can help individuals return to their recovery journey stronger than before.
Conclusion
Substance abuse treatment is a multifaceted process that provides individuals with the tools, support, and guidance necessary to overcome addiction. From detoxification and inpatient rehabilitation to outpatient therapy and support groups, effective treatment addresses the physical, psychological, and social aspects of substance use disorders. By embracing a personalized approach and committing to long-term recovery strategies, individuals can reclaim their lives, rebuild relationships, and achieve lasting well-being.
If you or a loved one are struggling with substance abuse, seeking professional help is the first step toward a brighter, healthier future. Recovery is possible, and with the right treatment and support, life after addiction can be fulfilling, empowered, and free from the grip of substance use.