Introduction
The rapid rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems has brought Black Mass a material composed of shredded battery components rich in lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese, and other critical metals into the spotlight. As the demand for these battery materials surges and supply chains face strain, Black Mass recycling offers a crucial pathway toward resource recovery, circular economies, and environmental sustainability.
Market Snapshot
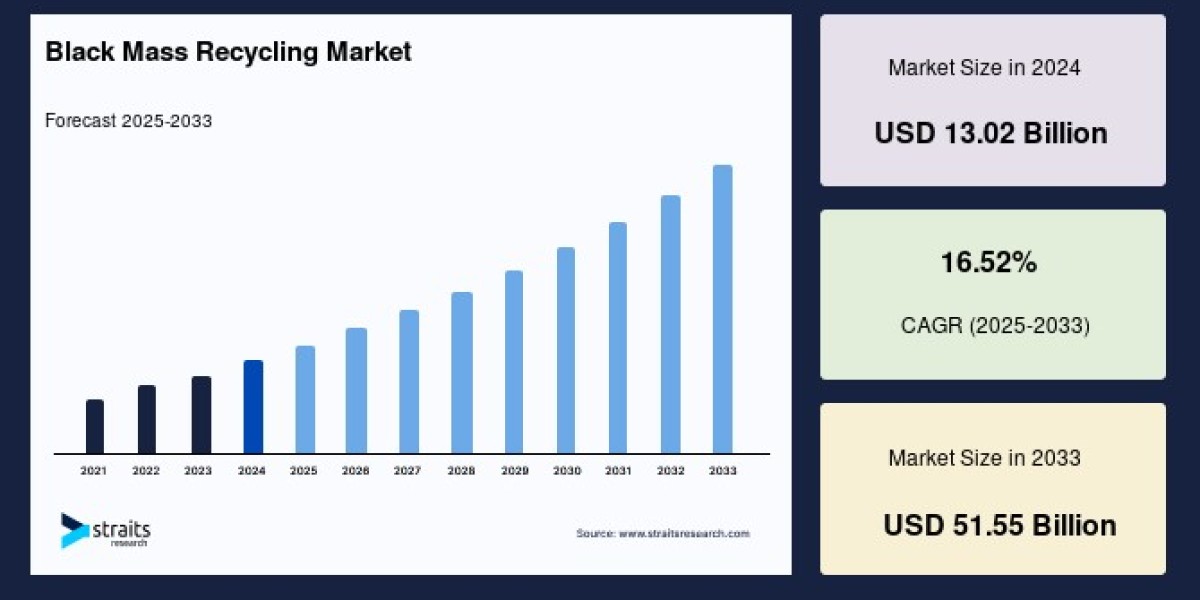
The global black mass recycling market size was valued at USD 13.02 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 15.17 billion in 2025 to reach USD 51.55 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 16.52% during the forecast period (2025–2033).
Key Growth Drivers
1. Rapid EV Adoption & Battery Waste Accumulation
The skyrocketing adoption of EVs has led to a surge in spent lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are a treasure trove of valuable metals. Without efficient recycling systems, reliance on virgin mining places strain on supply, cost structures, and geopolitics. Black Mass recycling directly addresses these challenges by transforming battery waste into reusable metal inputs.
2. Circular Economy and Regulation
Environmental concerns and policy responses are accelerating Black Mass recycling. For instance, a prominent region recently designated Black Mass as hazardous waste, enforcing stringent disposal and shipment regulations to prevent its export to non-member countries. From late 2026 onward, these rules will standardize handling and encourage localized recycling solutions, strengthening domestic supply resilience.
3. Emergence of Regional Recycling Hubs
Regional recycling hubs are gaining traction, designed to minimize logistics complexities and foster closed-loop material ecosystems. A leading recycler, based in North America, recently expanded its operations with the aim of producing 100 GWh-worth of recycled cathode materials annually by 2026 solidifying its role as a major domestic supplier.
4. Advancements in Processing Infrastructure
In Europe, a major chemical firm recently inaugurated one of the continent’s largest production plants for Black Mass, capable of processing 15,000 tons of spent lithium-ion batteries each year. Facilities like this are instrumental in laying the groundwork for scalable recycling and downstream chemical recovery.
Market Segmentation Overview
By Battery Type: Lithium-ion batteries dominate the segment. Nickel-based batteries are also included in the broader classification.
By Battery Source: Segmented into automotive batteries, consumer electronics, industrial batteries, and others with automotive batteries leading the way due to EV market momentum.
By Recycling Process: Divided between hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical methods, each offering different efficacy, cost, and environmental trade-offs.
By Recovered Metals: Includes lithium, cobalt, nickel, copper, and other metals, each crucial to battery production.
By Region: Categories include Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa.
Regional Dynamics
Asia‑Pacific
Asia-Pacific commands a dominant share of the Black Mass recycling market. The region’s stronghold on both EV production and battery manufacturing especially in countries such as China, South Korea, and Japan ensures abundant supply of spent batteries. Furthermore, policies such as a national battery waste management regulation are driving recycling capacity expansion by domestic players.
North America
With growing investments in domestic recycling capabilities and significant government incentives, North America is becoming a vital market for processing Black Mass. Several leading recyclers based here already handle a substantial share of regional battery recycling activities.
Europe
Europe is undergoing a strategic build-up of recycling infrastructure, underpinned by new environmental laws and effort to close supply chain loops. The recent commissioning of a major recycling plant underpins this ambition to capture more of the value chain within the continent.
Competitive Landscape
Key players shaping the industry include:
Leading pure-play battery recyclers that focus on high-efficiency Black Mass recovery.
Multinational chemical and materials companies integrating recycling into broader supply chain strategies.
Specialized firms offering hydrometallurgical or pyrometallurgical capabilities geared toward reclaiming battery-grade metals.
These companies are investing in capacity expansion, technology development, and geographic diversification to meet growing demand.
Recent Industry Highlights
Recent developments underscore the sector’s dynamism:
North America Expansion: A major recycler aims to produce enough recycled cathode-active materials to satisfy 100 GWh worth of production annually.
European Facility Launch: A large-scale Black Mass processing plant was launched, capable of handling tens of thousands of EV batteries annually a key step toward self-sufficient supply.
Industry Insights and Market Momentum
Discussions in industry forums reflect optimism and realism:
“Black Mass prices are closely tied to spot prices for battery-grade metals.” This underscores how market value is derived from its constituent materials.
These insights highlight how tightly Black Mass trading aligns with fundamental metal markets, influenced by global demand, supply disruptions, and commodity trends.
Opportunities & Challenges
Opportunities
Strategic Supply Security: Recycling reduces reliance on imported raw materials and stabilizes supply chains.
Climate & Resource Benefits: Recycling conserves natural resources, reduces mining impact, and supports net-zero goals.
Technological Innovation: Advances in direct recycling methods and refining processes are increasing efficiency and economics.
Policy Support: Regulations imposing recycled content mandates and recycling obligations are boosting demand.
Challenges
High Capital Investment: Establishing scalable recycling operations demands significant upfront infrastructure.
Regulatory Complexity: Long lead times and stringent compliance requirements can slow project deployment.
Process Efficiency Variations: Different battery chemistries and contaminant profiles make standardization difficult.
Market Volatility: Black Mass pricing is highly sensitive to fluctuations in underlying metal prices, adding financial risk.
Future Outlook
The Black Mass recycling market is set to undergo transformational expansion through 2033. Market size growth estimated to exceed USD 50 billion by decade’s end reflects both industrial scale-up and regulatory momentum.
As the world pivots toward sustainable and secure battery ecosystems, recycling will increasingly move from niche to core. Investment in technology, processing infrastructure, and cross-industry collaboration will determine which players shape the next generation of circular battery supply chains.
Conclusion
Black Mass recycling is no longer a fringe activity it’s foundational to the future of resource efficiency, battery manufacturing, and environmental stewardship. With growing incentives and technological maturity, it offers an economically viable and sustainable solution to one of our most urgent industrial challenges.