Introduction
Manganese, a critical industrial metal, is foundational for enhancing steel strength, manufacturing advanced batteries, producing fertilizers, and supplying essential chemicals. Its versatility and widespread use make its global market a vital component across multiple sectors. As infrastructure development accelerates and the electric vehicle (EV) revolution advances, manganese demand is surging, transforming market dynamics and supply chains alike.
Market Overview
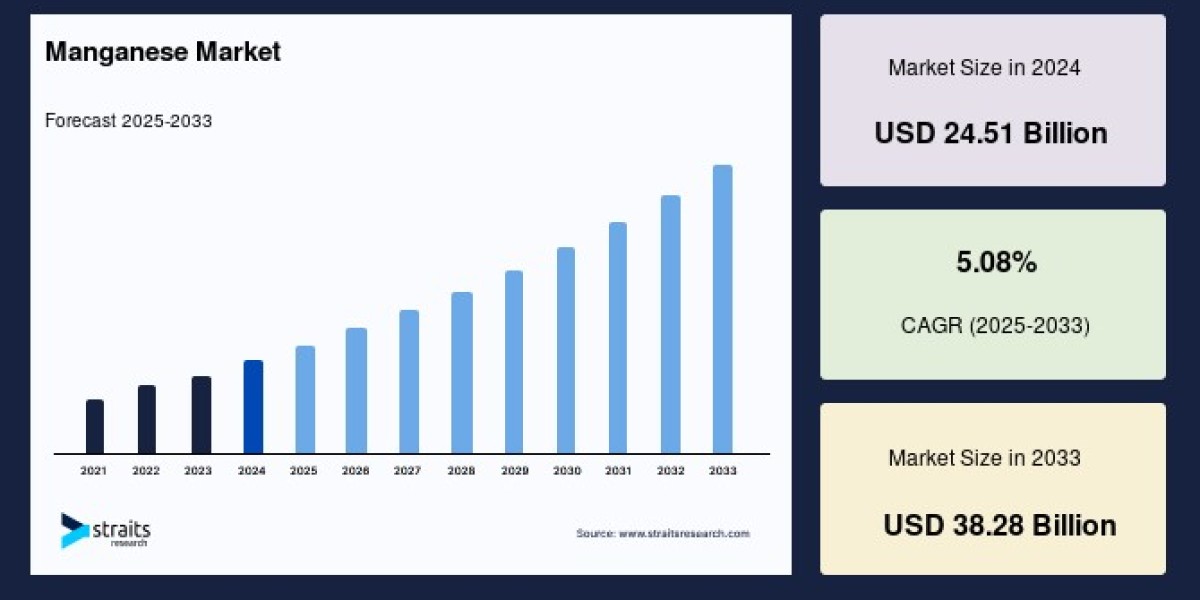
The global manganese market size was valued at USD 24.51 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 25.76 billion in 2025 to reach USD 38.28 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.08% during the forecast period (2025–2033). This upward trajectory is fueled by demand from industries such as steel manufacturing, agriculture, chemicals, and burgeoning technologies like EV battery production.
Market Drivers
1. Steel Industry: The Core Demand Driver
Manganese is indispensable in steelmaking, where it enhances properties such as tensile strength, hardness, and wear resistance. With global infrastructure and construction projects proliferating, especially in Asia and Africa, steel demand is surging, directly boosting manganese consumption.
2. EV Batteries: An Emerging Growth Engine
Manganese plays a major role in lithium-ion battery chemistries like Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC), valued for their cost-effectiveness, safety, and performance. Global EV sales continue to accelerate, pushing demand for battery-grade manganese compounds.
3. Agriculture and Chemical Applications
Manganese-based fertilizers represent vital micronutrients in crops such as soybeans, wheat, and corn, especially in fast-growing agricultural economies. Industrial chemical derivatives, including manganese sulfate and dioxide, are extensively used in batteries, ceramics, water treatment, and more.
4. Strategic Mineral Security and Sustainability
Governments are prioritizing supply chain resilience and sustainable industrial practices. Manganese is increasingly integrated into recyclable aluminum and copper alloys, aligning with green transition initiatives.
Segmentation Breakdown
By Type
Metallic Manganese
Non-metallic Manganese
By Grade
High-Purity (Battery Grade)
Medium-Grade
Low-Grade
By Application
Steel Manufacturing
Batteries
Chemicals
Fertilizers & Animal Feed
Others
By End-Use Industry
Construction
Automotive
Electronics
Energy & Power
Agriculture
Chemical Manufacturing
Others
By Region
Asia-Pacific (APAC)
North America
Europe
Middle East & Africa
Latin America (LATAM)
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific: Industry Powerhouse
The region dominates both production and consumption. Leading steel makers like China, with massive infrastructure initiatives, drive manganese demand in construction, transportation, and EV sectors. Countries like India and Indonesia further amplify this trend through growth in mining and battery materials.
North America
This is a mature yet evolving market, spurred by domestic investments in battery-grade manganese production, and demand from construction, automotive, and EV sectors is steadily rising.
Europe
Increasingly focused on high-purity manganese solutions, the EU is strengthening recycling and refining capacities to reduce dependency on imports and meet sustainability targets.
Middle East, Africa, Latin America
These regions are emerging players. With rich mineral reserves and expanding industrial activity (e.g., fertilizers in Brazil, construction in Africa), their influence is gradually increasing.
Key Industry Developments
Strategic acquisitions have marked a pivot toward critical minerals, with major mining companies investing heavily in manganese assets in key regions.
Supply disruptions due to natural events have prompted price spikes and production adjustments by global players.
Market Opportunities
Battery-grade manganese demand for EVs and energy storage is a fast-growing segment, attracting significant investment in processing infrastructure.
Advancements in specialty alloys such as aluminum-manganese bronze and copper-manganese materials open new manufacturing frontiers.
Sustainable mining and recycling initiatives are being adopted to enhance environmental responsibility and circular economy practices.
Challenges & Market Constraints
Environmental regulations and compliance costs are increasing, sometimes causing delays or suspensions in mining operations.
Price volatility caused by geopolitical instability and supply chain bottlenecks remains a significant challenge.
Declining ore grades in some regions threaten the availability of high-quality feedstock.
Emerging alternatives in battery and materials science could reduce manganese demand in the long term, though it remains essential currently.
Future Outlook
The market’s future depends on innovation in delivering battery-grade manganese, transitioning to sustainable production, and stabilizing supply chains. Companies investing in processing, recycling, and resilient logistics are best positioned to succeed.
Conclusion
Manganese remains a strategic commodity whose relevance spans traditional industries and emerging technologies. Its importance in steel production, battery chemistry, agriculture, and sustainability initiatives ensures its continued prominence in global markets.
Balancing growth with responsible stewardship will be key for all stakeholders in mining, manufacturing, and policy domains as the manganese market continues to evolve.