Introduction
The global seafood industry is undergoing a dynamic transformation, driven by shifting dietary preferences, rising demand for sustainable protein sources, and advances in food technology. At the forefront of this change is haddock a white-fleshed fish known for its mild flavor, flaky texture, and versatility in culinary applications. With its historical significance in Northern European diets and growing appeal in health-conscious markets, haddock has carved out a vital niche in both fresh and processed seafood segments.
The global haddock market is poised for substantial growth over the next decade. This article explores the forces driving this expansion, the challenges it faces, regional trends, innovation in processing, and what lies ahead for producers, processors, and consumers worldwide.
Market Overview and Growth Potential
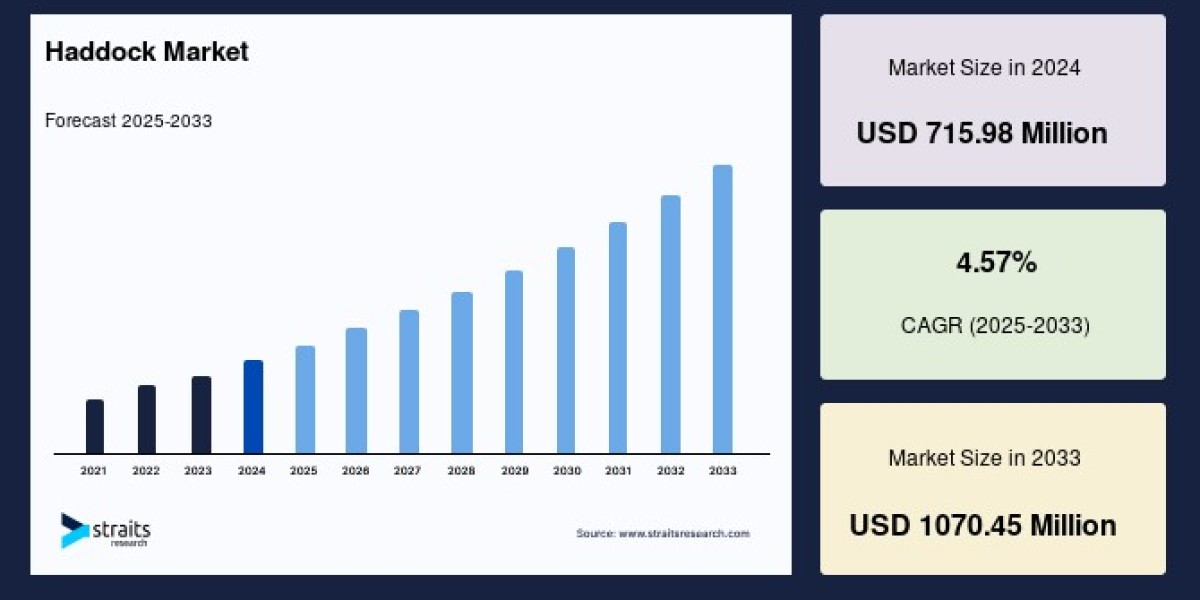
The global haddock market size was valued at USD 715.98 million in 2024 and is anticipated to grow from USD 748.70 million in 2025 to reach USD 1070.45 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.57% during the forecast period (2025–2033).
While haddock is still a relatively niche species compared to tuna, cod, or salmon, it is gaining ground rapidly due to:
Favorable nutrition profile
Culinary versatility
Availability in multiple forms (fresh, frozen, smoked, canned, etc.)
Advances in packaging and cold chain logistics
Key Drivers of Market Growth
1. Health and Wellness Trends
Consumers worldwide are shifting toward healthier diets, reducing red meat consumption, and seeking lean protein alternatives. Haddock is high in:
Protein
Omega-3 fatty acids
Vitamins B6 and B12
Low in fat and calories
This makes it an ideal choice for people managing heart health, weight, and diabetes.
2. Culinary Versatility and Convenience
Haddock is widely used in traditional dishes (such as British fish and chips and smoked haddock chowders) and increasingly features in modern recipes including:
Fish tacos
Ready-to-eat seafood salads
Grilled fillets
Frozen fish fingers
Microwave-ready meals
Its mild taste and firm texture allow it to absorb seasoning well, making it a favorite for food manufacturers looking to create diverse flavor profiles.
3. Growth in Foodservice Industry
Restaurants, hotels, and institutional food providers (such as airlines, hospitals, and schools) are incorporating more haddock into their menus. The fish’s consistency and availability in portion-controlled formats support large-scale cooking without compromising quality.
4. Sustainability and Eco-Labelling
As sustainability becomes a non-negotiable requirement in seafood sourcing, haddock fisheries in regions such as the North Atlantic (Norway, Iceland, UK) have invested in responsible fishing certifications like MSC (Marine Stewardship Council).
Consumers are more willing to pay a premium for products that are:
Sustainably sourced
Fully traceable
Certified by third parties
Haddock fits well into this narrative, especially compared to overexploited species.
Product Segmentation
The haddock market is segmented based on processing and packaging, offering multiple avenues for growth:
1. Fresh Haddock
Sold through fish counters and specialty seafood markets. Preferred in countries with strong local fisheries and cold-chain infrastructure.
2. Frozen Haddock
The most common form for exports. Modern freezing techniques preserve taste and texture, expanding reach to inland and export markets.
3. Smoked Haddock
A premium product used in gourmet recipes and traditional European dishes. Increasing demand for artisan and naturally smoked variants.
4. Canned Haddock
Less common globally but offers portability and shelf stability. Gaining popularity in parts of Asia and Africa.
5. Breaded or Battered Products
High convenience products like fish fingers, fish cakes, and pre-breaded fillets are fueling growth among families and foodservice buyers.
Distribution Channels
The haddock supply chain encompasses multiple routes, including:
Supermarkets and Hypermarkets: Largest share of retail sales, often under private labels.
Specialty Seafood Stores: Offer higher-quality, fresh, or artisanal smoked haddock.
Online Retail Platforms: A rapidly growing channel, offering delivery of frozen and pre-cooked meals.
Foodservice Distributors: Bulk purchasing by restaurants, hotels, schools, and institutions.
Export Channels: Haddock is traded globally, especially from European producers to North America, Asia, and Africa.
Regional Market Insights
Europe
Europe remains the largest producer and consumer of haddock. Key countries include:
UK: Largest consumer, with haddock being a staple in fish and chips.
Iceland and Norway: Leading exporters with strong fisheries management.
France and Germany: Growing markets for value-added and frozen haddock.
North America
Demand is driven by:
Health-conscious consumers
Immigrant populations familiar with haddock
Restaurant adoption of haddock-based dishes
The U.S. and Canada are both growing markets for frozen, smoked, and breaded haddock.
Asia-Pacific
An emerging market with rising seafood consumption. Countries like China, South Korea, and India are exploring haddock as a lean protein source in both traditional and fusion cuisine.
Middle East & Africa
Demand is lower but rising particularly in urban centers and among affluent consumers seeking imported, high-quality seafood.
Challenges Facing the Haddock Market
Despite strong growth potential, the haddock industry faces several challenges:
1. Environmental Factors
Climate change is shifting haddock migration patterns and affecting fish stock distribution.
Rising ocean temperatures may reduce catch volumes in traditional zones.
2. Regulatory Pressures
Quotas and fishing restrictions are imposed in regions like the Gulf of Maine to manage stock levels, potentially limiting supply.
3. Competition from Other Species
Cheaper and more widely available fish like tilapia, basa, and cod offer stiff competition in price-sensitive markets.
4. Consumer Awareness
Outside Europe, many consumers are unfamiliar with haddock. Marketing efforts are needed to promote it as a healthy, delicious, and sustainable alternative.
Opportunities for Growth
1. Product Innovation
Ready-to-cook kits, flavored frozen fillets, and portion-controlled packs are attracting younger and time-poor consumers.
Smoked and gourmet variations cater to premium markets.
2. Export Market Development
African and Southeast Asian countries are untapped regions for haddock exports, especially frozen and canned formats.
3. Sustainable Branding
Brands emphasizing traceability, eco-certification, and ocean-friendly sourcing will win consumer trust and loyalty.
4. Strategic Collaborations
Partnerships between fisheries, processors, and food brands can help streamline the supply chain and reduce costs.
Future Outlook
The haddock market is positioned for long-term growth. As consumers continue to seek sustainable, nutritious, and convenient foods, haddock meets all three criteria. The expansion of e-commerce, improved logistics, and value-added processing will further boost accessibility and demand.
With smart investments in sustainability, technology, and marketing, haddock could become not only a household staple in its traditional markets but a globally recognized name in the healthy seafood sector.
Conclusion
The global haddock market reflects the broader transformation of the seafood industry where sustainability, health, and convenience converge. From frozen fillets to gourmet smoked cuts, haddock has demonstrated its ability to evolve with consumer needs and market demands.
Looking ahead, strategic innovation and responsible resource management will be key to unlocking the full potential of this mild yet mighty fish on dinner plates around the world.