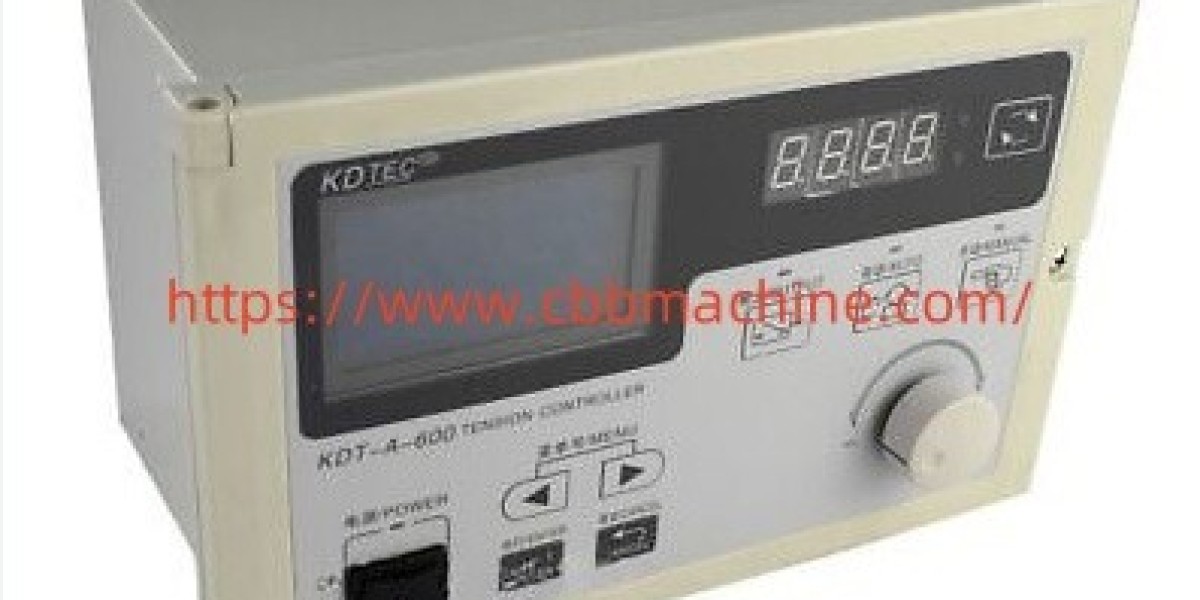
In modern web guiding systems, the Tension Controller plays a central role in maintaining stability and material consistency during high-speed production processes. From paper manufacturing to film slitting, this component is essential for regulating and adjusting the tension exerted on materials as they move through rollers, preventing wrinkles, breaks, or misalignments that could lead to costly waste or machine downtime.
Tension control is the process of managing the force applied to a continuous material—commonly paper, plastic, textile, or metal strip—through its journey on a converting or printing line. As speed, load, or material width changes, maintaining consistent tension becomes increasingly difficult without a smart, responsive system. That's why installing a reliable controller improves overall productivity, ensuring the quality and uniformity of the final product.
There are typically three main types of tension control methods used in industries: open loop, closed loop, and semi-closed loop. Open-loop systems rely on pre-set parameters and do not adjust in real time. Closed-loop systems, on the other hand, use sensors and feedback from load cells or dancers to make live adjustments. Semi-closed loop systems combine aspects of both for moderate precision needs. The selection of a proper controller depends heavily on production demands, material type, and sensitivity.
One of the most critical advantages of a well-integrated tension control system is its ability to reduce material waste. Without precise tension control, products may suffer from edge waviness, telescoping rolls, or inconsistent thickness. This becomes especially problematic in high-speed applications where minor errors multiply rapidly. By minimizing stretch or slack, a controller ensures that your substrate remains smooth and tightly guided throughout its processing route.
Moreover, modern tension controllers often integrate digital control panels, allowing operators to fine-tune parameters with ease. With programmable settings, real-time monitoring, and automatic response to sensor data, the latest controllers are more adaptive and user-friendly than earlier models. Some systems also support communication with other factory equipment, enhancing automation and reducing manual intervention.
Industries that benefit from advanced tension control include paper converting, film extrusion, battery electrode production, textile winding, and metal foil handling. In these sectors, maintaining constant web tension is not merely a technical improvement—it is a necessity for meeting quality standards and client expectations.
Maintenance of tension controllers is equally important to ensure long-term operation. Dust build-up, wear on sensors, or software misconfigurations can lead to inaccurate readings or inconsistent outputs. Routine inspection and recalibration help preserve performance and protect other machinery in the line from stress-related wear.
As automation continues to evolve, tension control systems will likely integrate even deeper with AI-driven process optimization and predictive maintenance. Manufacturers are already exploring adaptive tension algorithms that learn from usage patterns to predict and avoid failure. This trend highlights the growing importance of such systems in Industry 4.0 settings.
For a deeper dive into different types of tension controllers and their applications, visit https://www.cbbmachine.com/news/industry-news/tension-controller-types-importance-applications-and-more.html