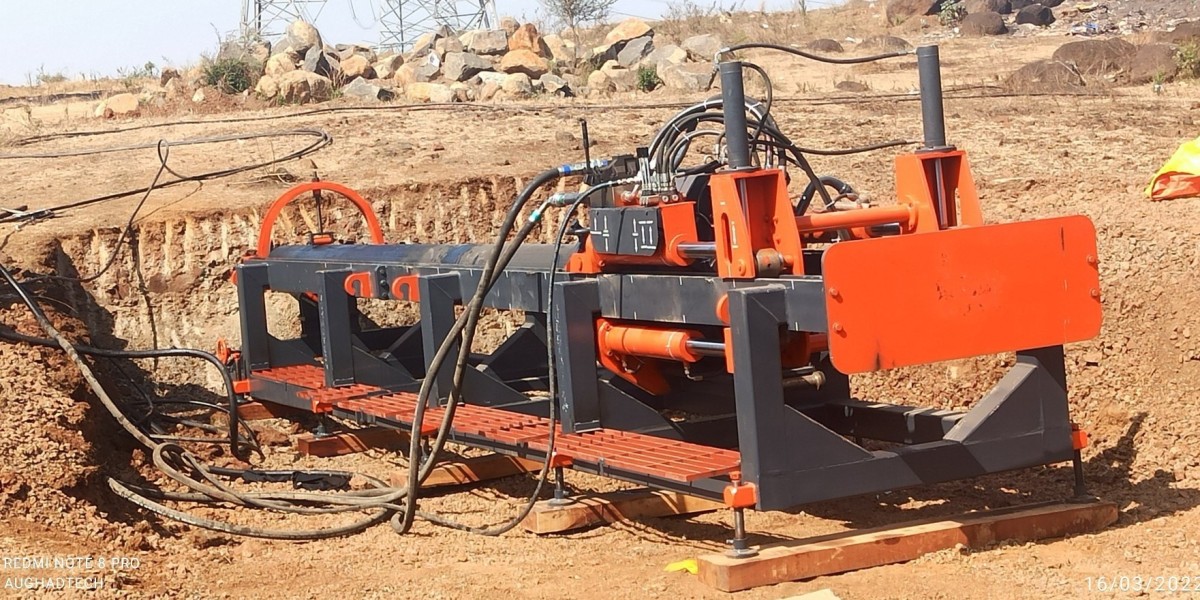
Trenchless technology has revolutionized underground construction methods, and one of the most commonly used machines in this process is the horizontal auger boring machine. Designed to install steel casing or pipes under roads, railways, and other obstructions without disturbing the surface, this equipment offers accuracy and minimal disruption. However, operating a horizontal auger boring machine safely requires specific knowledge, proper planning, and strict adherence to safety guidelines.
This guide aims to provide beginners with a comprehensive understanding of how to safely operate a horizontal auger boring machine, including preparation, operation, and post-operation practices.
What Is a Horizontal Auger Boring Machine?
A horizontal auger boring machine is a powerful tool used for trenchless pipe installation. It works by rotating an auger inside a casing pipe, removing soil as the casing advances horizontally underground. The soil is transported back through the casing to the entry point, where it is discharged.
This method is particularly suitable for shorter bores with minimal surface disturbance and is widely used in urban infrastructure, utility installation, and roadwork projects.
Pre-Operation Safety Checks
Before operating the horizontal auger boring machine, a thorough safety inspection is necessary to reduce the risk of equipment failure or workplace accidents.
Site Survey
Assess the job site for obstacles such as underground utilities, water lines, and electrical cables. Utility maps and ground-penetrating radar may be used to confirm safe bore paths.Soil Testing
Conduct soil analysis to ensure that the ground conditions are suitable for auger boring. Loose or highly compacted soils may require special considerations or equipment modifications.Equipment Inspection
Check the machine for mechanical issues. Inspect the auger flights, bearings, casing components, and hydraulic systems for wear or damage. Ensure all safety guards are securely in place.Safety Gear
Operators and crew should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including hard hats, gloves, steel-toed boots, high-visibility clothing, and hearing protection.Training and Communication
Make sure that all team members are trained in the operation of the horizontal auger boring machine and aware of the communication signals or protocols used during the operation.
Safe Operating Procedures
Proper operation of a horizontal auger boring machine involves a series of steps that must be followed methodically. Here's a step-by-step look at how to perform the boring process safely:
Machine Setup
Position the machine on a level and stable surface.
Anchor the machine properly using ground stakes or steel plates to prevent shifting during operation.
Align the machine with the intended bore path using lasers or manual surveying techniques.
Starting the Bore
Begin by cutting the entry point and setting the casing pipe at the correct angle and elevation.
Power up the machine and slowly start rotating the auger.
Gradually advance the casing while monitoring torque and rotation speed.
Soil Removal
The auger conveys soil back to the pit, where it is collected and disposed of properly.
Make sure the spoil is not blocking the exit point or overwhelming the system.
Avoid sudden increases in pressure or torque, which can indicate obstructions or overloading.
Monitoring During Boring
Constantly check for machine vibrations, unusual noises, or torque fluctuations.
Watch for soil inconsistencies that might suggest unexpected voids or boulders.
Use lasers or tracking systems to ensure the bore remains on course.
Communicating with the Crew
Keep constant communication between the operator and pit crew.
Use hand signals, two-way radios, or other reliable methods to coordinate movements and alerts.
Emergency Preparedness
Even with the most careful preparation, emergencies can arise. It is essential to be prepared for possible complications:
Hydraulic Leaks or Mechanical Failures
Stop operations immediately if leaks or mechanical failures are detected. Hydraulic fluid is flammable and under high pressure, which can cause serious injury.Auger Stoppage
If the auger stops moving, do not try to restart it immediately. Shut off the machine, inspect the system, and remove any obstructions before resuming.Unexpected Utility Strikes
If a utility line is hit, stop all activity and notify the appropriate utility provider. Do not attempt to handle electrical or gas lines without professional support.
Post-Operation Safety
After the bore is complete, it is crucial to wrap up the job with safe post-operation procedures:
Shutdown Process
Power down the machine carefully, following manufacturer instructions.
Release hydraulic pressure before performing maintenance or removing components.
Cleanup and Maintenance
Clean augers and casing pipes to prevent soil buildup or rusting.
Inspect the machine for damage and schedule repairs if necessary.
Record machine hours and maintenance tasks for future reference.
Site Restoration
Restore the entry and exit pits as per the project requirements.
Remove all equipment and materials from the site to avoid safety hazards.
Final Thoughts
Operating a horizontal auger boring machine safely is a skill that combines technical understanding, physical awareness, and adherence to safety protocols. Beginners must respect the power of the machinery and the complexity of underground work. Through careful planning, proper equipment checks, and clear communication, operators can achieve successful bore completions while maintaining a safe job site.